For people who haven't experienced virtual reality, it's hard to explain what active presence is. So in this quick guide, we will explain what active presence in VR feels like and what to expect.
Active presence is also known as hand presence, it basically means an immersive state when putting on a VR headset while feeling like you're inside the experience.
Presence is the subjective feeling of “being there” within a constructed virtual environment and behaving and feeling as if this mediated environment was the real world. The illusion is perceptual but not cognitive.
Increased Feeling Of Presence And Agency

A well-designed VR experience allows users in a particular career field to increase their skill level through virtual reality training. There are studies done on the relationship between presence and agency, and presence and skills improvement through active and passive VR simulations. The studies have found active stimulation induces a higher level of general presence and agency, and no skill improvement was evident in those tests due to the short training period.
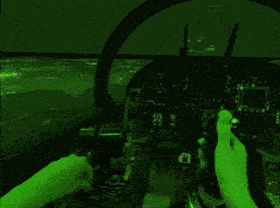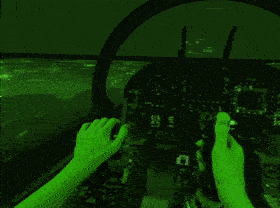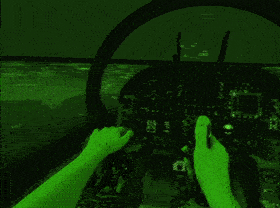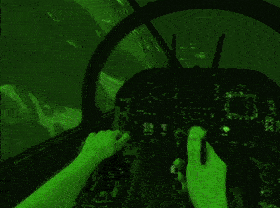
However, when hardware setup is as close to real world as possible, there is a transfer of skills to a real-world environment. These are things beyond just simple games people can play with VR controllers, and these are flight simulators with mixed reality setup, where the user can actually interact with switches and handles like the real thing, and we call it active VR.
Active VR
To further increase the realism until the user can't tell the difference between real or fake still takes years of development, but it's for sure that there are 7 major elements to consider:
- Presence
- Immersion
- Embodiment
- Free movement
- Shared space
- Dynamic spectating
- Depth of Field
Presence

Presence is about feeling actually existed inside an environment, and we can maximize this by increasing VR display definition, wide field of view, accurate tracking to prevent VR motion sickness, and of course a well designed VR experience
Immersion

Immersion is about feeling surrounded by sound and stimuli that make the brain believe the environment. Overall it's the perception that a digital environment really exists. To maximize immersion, a well-designed VR experience is a must, which includes storytelling, high fidelity graphics, lifelike rendering, haptics, smell, auditory experience, advanced lighting, and many more things that you would expect in the real world.
Free Movement

Free movement is about creating a completely unbounded interaction from physical restrictions in the outside world. The user can freely explore and move around in the digital environment with 360° mobility. Currently, VR games have 6 degrees of freedom, but 360° videos don't. Volumetric VR video will significantly change that in the near future.
Embodiment
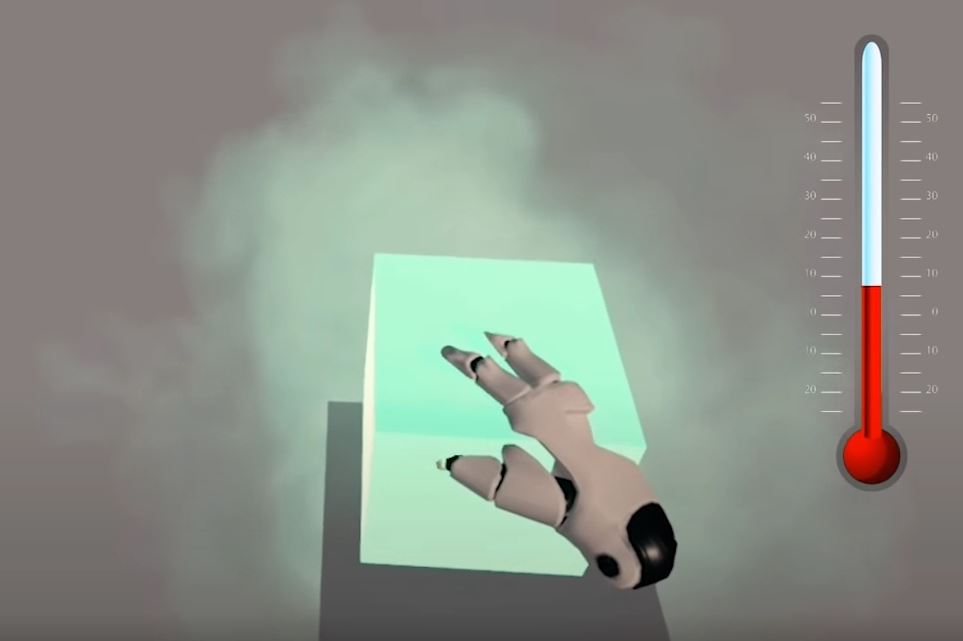

Embodiment is about experiencing a virtual body within the VR environment using the precise tracking technology that aligns with your real body so what you see doesn't conflict with how you feel.
Shared space

Shared space provides the human perception that the user is interacting with other people in a digital environment. Experiences like a copilot, VR chat, multiplayer gaming, meeting room, VR public speaking, and many more.
Dynamic spectating

Dynamic spectating is about viewing others in VR while exhibiting all other 5 elements. Experiences like this will take audience experience to a new level for live news, live youtube videos and many more.
Depth Of Field
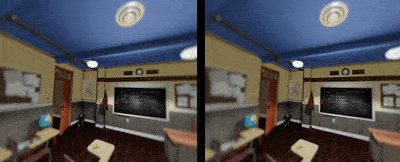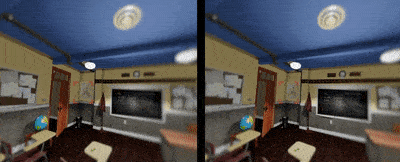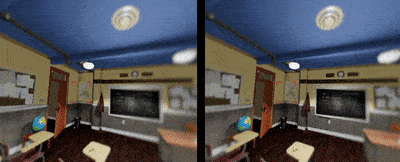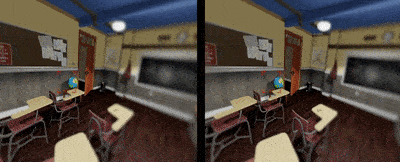
Depth of field can further increase the immersive experience for users to tell spatial relationship inside a digital environment. Currently foveated rendering is about to make this happen by sharpen on the image where the eye is looking and blur out the rest to save computing power.
